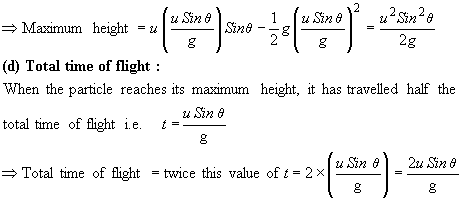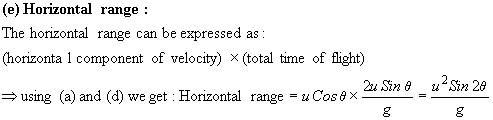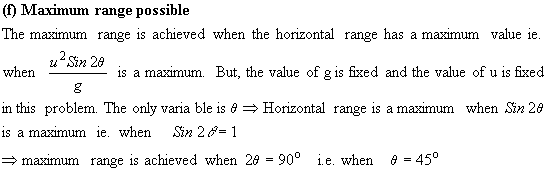Projectiles are particles which are projected under gravity through the air. Examples of projectiles include objects thrown by hand or shells fired by a gun. Typically the mechanics problems involving projectiles with both horizontal and vertical velocity components and are subject to a downward vertical acceleration of g. It is assumed there is no air resistance to a projectile’s motion.
Projectiles
Sample Problem: Projectile
A particle is projected at an angle q to a horizontal plane as shown in Fig. 1. If u is the initial velocity of projection and we assume there is no air resistance, find expressions for:
- Horizontal and vertical components of velocity after time t
- Horizontal and vertical components of displacement after time t
- Maximum height reached
- Total time of flight
- Horizontal range
- Maximum range possible
Solution
Fig. 1 illustrates the physical model of the projectile’s motion and provides the basis for constructing equations whose solution makes it possible to answer the individual parts (a) ?(f):
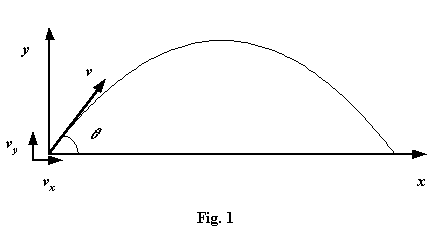
The components of velocity are shown in Fig. 1 where the x-axis represents the horizontal plane and the y-axis, the vertical plane. We can use the format of equations derived in Section 1: “Velocity and Acceleration”:
Where:
v = velocity at any time t
u = Initial velocity
a = Acceleration = –g
s = distance travelled in time t
Consider the following equations of motion:
(i) v = u + at (ii) v2 = u2 + 2as (iii) s = ut +![]() at2
at2
(a) Horizontal and vertical components of velocity after time t
Horizontal component of velocity = vx = u Cos q (this component is not subject to gravity and remains constant throughout the projectile’s flight)
Vertical component of velocity (from (i)):= vy = u Sin q – gt
(b) Horizontal and vertical components of displacement after time t
Horizontal component of displacement = x = vx t = ut Cos q
Vertical component of displacement (from (iii)) = y = vy t = ut Sin q ?![]() gt2
gt2
The equations derived in (a), (b) above are used to derive answers to parts (c) ?(f):
(c) Maximum height reached:
At maximum height, vy = 0 Þ u Sin q – gt = 0
Þ Time elapsed to reach maximum height, t = ![]()
Þ To calculate maximum height, put this value of t into the expression for y derived in (b) above: